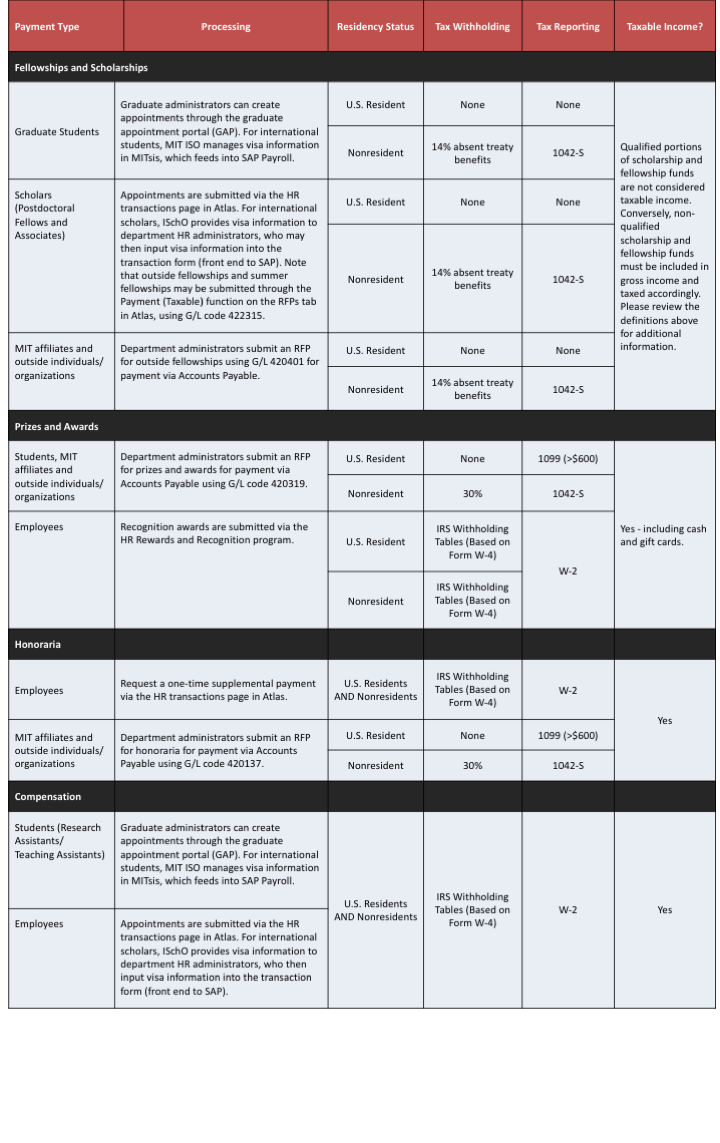
Grants are payments given to an eligible grantee, which may be a student, MIT affiliate, or other organization, for a designated purpose. Grants include the payment types listed below, as well as a few others. It is important to determine the specific type of grant in order to ascertain the proper taxability and reporting requirements.
A stipend is a general term that is not specifically defined by the IRS. Stipends may refer to any or multiple payment types. Therefore, you will need to determine the appropriate payment type as defined below.
Scholarships are amounts paid or allowed to a student for the purpose of study. Scholarship funds are intended to offset the cost of a student’s education for an upcoming or current academic year. Amounts paid by degree candidates for qualified expenses such as tuition, fees, and expenses required for coursework are not considered taxable income to the recipient. Conversely, amounts paid for non-qualified expenses such as room and board must be included in gross income and taxed appropriately.
Fellowships are amounts paid or allowed to an individual for the purpose of study or research. At MIT, fellowship payments are often referred to as “grants” or “awards” but if these payments are earmarked for study or research, they may be considered fellowships. Amounts paid by degree candidates for qualified expenses such as tuition, fees, and expenses required for coursework are not considered taxable income to the recipient. Conversely, amounts paid for non-qualified expenses such as independent research travel expenses are included in taxable gross income.
- Targeted grants are amounts issued for activities undertaken in the public interest, not primarily for the private financial benefit of a specific person(s). These amounts are generally not taxable to the recipient.
- If the fellowship requires certain services to be performed, it may be partially compensation income.
- Fellowship payments issued to nonresidents are subject to a 14% withholding tax.
Prizes and awards are amounts paid in recognition of an outstanding achievement or winnings in a competition, raffle, or other contest. When paying a prize or award, it is generally for a past performance. However, if the amount is intended for use in future research or study, the payment may be more properly categorized as a scholarship or fellowship.
- Exceptions – Tangible personal property given to employee for length of service or safety. See the restrictions at https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p5137.pdf.
- Cash or gift cards are always taxable.
The Details
Grants are payments given to an eligible grantee, which may be a student, MIT affiliate, or other organization, for a designated purpose. Grants include the payment types listed below, as well as a few others. It is important to determine the specific type of grant in order to ascertain the proper taxability and reporting requirements.
A stipend is a general term that is not specifically defined by the IRS. Stipends may refer to any or multiple payment types. Therefore, you will need to determine the appropriate payment type as defined below.
Scholarships are amounts paid or allowed to a student for the purpose of study. Scholarship funds are intended to offset the cost of a student’s education for an upcoming or current academic year. Amounts paid by degree candidates for qualified expenses such as tuition, fees, and expenses required for coursework are not considered taxable income to the recipient. Conversely, amounts paid for non-qualified expenses such as room and board must be included in gross income and taxed appropriately.
Fellowships are amounts paid or allowed to an individual for the purpose of study or research. At MIT, fellowship payments are often referred to as “grants” or “awards” but if these payments are earmarked for study or research, they may be considered fellowships. Amounts paid by degree candidates for qualified expenses such as tuition, fees, and expenses required for coursework are not considered taxable income to the recipient. Conversely, amounts paid for non-qualified expenses such as independent research travel expenses are included in taxable gross income.
- Targeted grants are amounts issued for activities undertaken in the public interest, not primarily for the private financial benefit of a specific person(s). These amounts are generally not taxable to the recipient.
- If the fellowship requires certain services to be performed, it may be partially compensation income.
- Fellowship payments issued to nonresidents are subject to a 14% withholding tax.
Prizes and awards are amounts paid in recognition of an outstanding achievement or winnings in a competition, raffle, or other contest. When paying a prize or award, it is generally for a past performance. However, if the amount is intended for use in future research or study, the payment may be more properly categorized as a scholarship or fellowship.
- Exceptions – Tangible personal property given to employee for length of service or safety. See the restrictions at https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p5137.pdf.
- Cash or gift cards are always taxable.